
Lesson 4. Magnetotherapies
4.1 What is Magnetotherapy
Magnetotherapy refers to the use of magnetic fields to help restore or maintain human health. So under this term we can include a great variety of techniques, from the ancient magnetotherapy that Cleopatra used by placing a magnetic stone on her forehead to preserve youth and beauty; to modern devices that generate pulsating magnetic fields. And we can also include a wide variety of magnetic products and accessories that are for sale as anyone can use them.
That is, any therapy that uses magnets of any kind to help maintain health, even Biomagnetism, is a type of magnetotherapy. But before studying medical Biomagnetism in depth, we are going to give an overview of some types of magnetotherapy and their benefits.
4.2 Magnetic accessories
Currently on the market there are a wide variety of accessories such as magnetic bands, bracelets, water jugs, sleeping mats, knee pads, etc. In most cases these are permanent magnets, which generate magnetic fields of moderate intensity 200 - 5000 Gauss, which makes them safe to use for everyone. These products have a beneficial effect since they help to balance and tone the biomagnetic energy of the user in a very general way; such is the effect of magnetic bracelets, sleeping mats or jugs. Other products have been designed to be used in a specific part of the body, to help regenerate a joint or muscle, such as knee braces or magnetic bands.

Some simply call magnetotherapy to the application of permanent magnets like the ones just described. We could call it a type of generic therapy, since it is not focused on any specific condition, but can be used in a general way to balance and harmonize the body's energy. Because it has practically no contraindications, it can be applied without a prescription, just follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
4.3 Magnetotherapy in physiotherapy
Magnetotherapy is used successfully to treat injuries to the musculoskeletal system. But it requires special devices capable of generating magnetic fields with special characteristics such as: frequency; the emission of the field either continuously or pulsed; the pulse shape (sinusoidal, semi-sinusoidal, rectified sinusoidal, square etc.) and the application time. Many of these devices have the possibility of generating different variants of magnetic fields, which the therapist will choose according to the patient's needs.
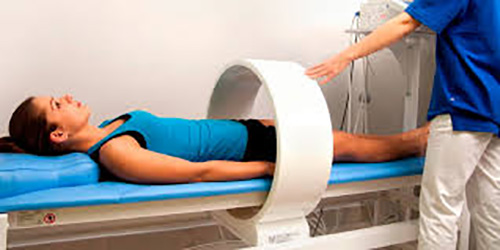
4.4 Benefits of magnetotherapy
Given the benefits offered by magnetotherapy (with pulsating magnetic fields) we allow ourselves to state its main effects, which is why it is widely used in physiotherapy and sports therapy:
4.5 Effects of the negative and positive pole

Richard Broeringmayer, based on various experiments, was able to establish the differences between applying a magnetic field with the positive pole of the magnet or with the negative pole. In his book "Principles of Magnetic Therapy" he presents the Nexts conclusions:
The negative pole (black, north) has a sedative, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect, favors relaxation and softening of tissues
The positive pole (red, south) is energizing, favors blood supply and gives vitality to organs and tissues, favors the contraction and solidification of tissues. The positive pole should not be applied for a long time.
Contraindications: (pole +)
1) Do not apply for a long time, greater than 25 minutes.
2) Do not apply if there is infection, inflammation or pain in the tissue.
Negative (-): |
Positive (+): |
|
|
Complementary activities: