
Lesson 5. Health and energy balance
5.1 Homeostasis
Our body, like any living organism, has the ability to self-regulate and seek a state of dynamic balance, which is known as homeostasis. In turn, each cell is a tiny living being that also seeks its own balance. So our body has to assure that the millions of cells that compose it, as well as the entire system as a whole, work in harmony. To achieve this, it resorts to complex mechanisms and systems such as the hormonal and nervous systems, which allow it to achieve a balance of temperature, heart rate, level of acidity or alkalinity (pH), hydration, etcetera. In reality, the human body has evolved to maintain a state of balance and health; it is due to our bad habits such as an inadequate diet, lack of exercise, stress and polluted environments that cause most diseases. To understand this we must study what is the bioenergetic balance.
5.2 Chemistry principles
 The bioenergetic balance is based on concepts of chemistry and electrical particles.
The bioenergetic balance is based on concepts of chemistry and electrical particles.
All matter is made up of basic elements called atoms, which also are made up of a nucleus and an "electron cloud". In the nucleus there are positively charged particles: protons (p +), and neutrons (n) with no electric charge. While the electrons that "spin" around the atom have a negative charge (e-).
Each element in nature has a different number of protons and electrons, as we can see in the periodic table. Based on the laws of chemistry we can determine the electronic configuration of an element according to the maximum number of electrons it can have in each orbit (electronic orbital = area of the atom where an electron is likely to be found), which in turn we can determine based on the number of electrons in each sublevel. Let's imagine that the orbitals are like boxes and within each box there can be different compartments (subdivisions).
- Orbital 1: = 2 electrons
- Orbital 2: 2+6 = 8 electrons
- Orbital 3: 2+6+10 = 18 electrons
- Orbital 4: 2+6+10+14 = 32 electrons…
- So on, until we reach the 7 orbital.
Do not worry if you do not fully understand the mathematical part, the important thing is to keep in mind that each element has a number of protons and electrons, which usually coincide. In which case the positive charges of the protons in the nucleus compensate the negative charges of the electrons that are in the orbits, and as a result the atoms have no electrical charge.
The number of protons (and electrons) is what is known as atomic number and according to it is how the orbits are “filled”, from the lowest with hydrogen with a single electron; up to the highest known so far the Oganeson with atomic number 118.
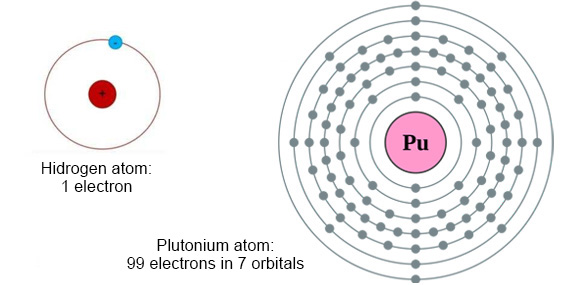
Based on these characteristics, all known elements can be classified in the periodic table. The periods (rows 1-7) correspond to the number of orbitals that the elements of the table have. While columns (1-18) indicate the groups to which they belong, which due to their characteristics can be classified into:
- Metals
- Non metals
- Metaloids
- Inert elements, rare gases or noble gases (column 18)

The structure of an atom depends on the configuration of its electrons and will determine how it behaves and reacts to other substances, its ability to combine with other elements (valence). Each atom will try to have 8 electrons in its last orbit, which it will achieve by joining with other atoms, forming molecules.
Noble gases, as they already have 8 electrons in their last orbit, do not need to combine with others, therefore they are the most stable elements in nature.
Those that need to "gain electrons" are metals. While those that need to give them are the non-metals, and therefore they have a negative charge and tend to be alkaline. In the center are the metalloids, which depending on the circumstances can gain or lose electrons.
Based on the principles of electrical charges in atoms, we can understand chemical reactions, which in turn are the basis of biochemistry.
5.3 What are ions
Ions are elements (monatomic) or molecules (polyatomic) that have an electric charge, this happens when their number of protons and electrons is not the same; that is, when they lose or gain an electron as a result of a reaction called ionization . There are two types of ions depending on whether they have a positive or negative charge:
- Anion or negative ion. It is when an atom or molecule acquires an electron, its charge becomes negative (-).
- Positive ion or cation. It is when an atom or molecule loses an electron, then its charge becomes positive (+).
5.4 Ions and metabolism
 In our body, ions are involved in multiple metabolic processes; They help maintain fluid balance in the body, allowing the passage of substances and liquids through the cell membrane, which is known as osmotic balance . They participate in the nervous impulse, in the muscular contraction and the absorption of nutrients through the membranes. They help maintain the acid-base balance.
In our body, ions are involved in multiple metabolic processes; They help maintain fluid balance in the body, allowing the passage of substances and liquids through the cell membrane, which is known as osmotic balance . They participate in the nervous impulse, in the muscular contraction and the absorption of nutrients through the membranes. They help maintain the acid-base balance.
Some such as salt, Sodium Chloride (NaCl), dissolves when it comes into contact with water and the atoms that remain are Chlorine ions, with a negative charge (Cl-) and Sodium with a positive charge (Na +). You may have already noticed that when it comes to an ion, a plus or minus sign is placed after its Letter.
Let's see the most important ions for our body and its functions.
5.4.1 Potassium K + Participates in muscle contraction, nerve conduction, regulates heart rate, energy production and the formation of genetic material.
5.4.2 Chlorine Cl- Activation of the nervous impulse, maintenance of osmotic pressure and acid-base balance, it is part of gastric secretion as it is part of hydrochloric acid.
5.4.3 Magnesium Mg + Intervenes in reactions that produce energy, helps bone growth and muscle contraction, activates vitamins and enzymes, essential in the formation of bone and dental structures, proteins and antibodies. Helps provide viscosity to synovial fluid (joints), Helps in lipid synthesis.
5.4.4 Calcium Ca+ It is essential for the development of bones and teeth, essential for the functioning of the nervous system, the muscular system, the heart and the immune system.
5.4.5 Sodium Na + helps the osmotic balance, necessary for the transmission of nerve impulses, intervenes in the muscular response.
Ions are also called electrolytes and it is very important that they are in balance in our body so that it can function optimally. The body will use various mechanisms and systems to keep them within the required limits, either through hormones, the nervous system, elimination through the kidneys and sweat, or by storing them in some tissues, such as calcium and phosphorus, which are stored in the bones.
It is also important to maintain a proper diet. A diet with excess Cl-Na, salt makes the tissues tend to retain fluids; then the cells must use more energy to maintain osmotic balance via the sodium-potassium pump. The amount of energy an adult uses at rest to maintain this balance is estimated to range from 20% to 40%.
5.5 Ions in the natural environment
Ions can also be formed by ionization processes of water or air molecules. This happens all the time in nature because of the movement of water, solar ultraviolet radiation, cosmic rays, energy from the Earth, lightning and also due to the role of chlorophyll in plants. In air, the proportion of ions is 4 anions per 1 cation, this balance is necessary for the existence of all living beings in the biosphere. Negative ions (anions) are found in nature in places such as rivers, waterfalls and forests, the simple fact of breathing deeply in one of these environments fills our body with beneficial ions.

Oxygen, when it is presented as a negative ion, is better assimilated, since blood contains iron with positive polarity, in this way O- and Fe + attract each other. Just to mention an example.
In summary, negative ions are very beneficial for our entire organism, favoring various systems such as respiratory, nervous, immune, cardiovascular, sexual ... even improving the mood, favoring relaxation and mental clarity.
On the other hand, positive ions weaken our body, causing fatigue, headaches, drowning, allergies, a tendency to depression, nervousness, insomnia ... Some sources of positive ions or cations are electrical and electronic devices; and in general the environment of cities and industry. In part, this is because negative ions stick to dust particles and decrease in polluted city and factory air. The use of air conditioning, synthetic materials in furniture and clothing create a large cation load. Positive ions are also created by the movement of strong winds or colliding air masses, which occurs many times before storms. Some very sensitive people are able to perceive the presence of these cations in their bodies, either as pain, dizziness, fatigue, etc.
5.6 Radicals and oxidative stress
Radicals (formerly free radicals) are atoms or molecules that have an unpaired electron, this makes them highly reactive; and for the same reason, they are short-lived. Radicals are created from chemical processes such as oxidation or by ultraviolet radiation. Polluted environments in cities or industrial areas, as well as a diet based on processed foods exposes the body to a greater amount of radicals. Since they are highly reactive elements, they damage organic molecules, causing chain reactions, which mainly affect cell membranes and DNA molecules.
Ultimately, this ongoing damage produces what is now known as oxidative stress. Our body, when subjected to radicals, reacts by generating a process of inflammation. Inflammation is a natural process by which cells react to aggressive situations, in this case radicals. The problem is when inflammation becomes chronic, then the body is no longer able to return to a state of ballance maintaining altered metabolic processes that involve excessive wear. If this situation is maintained for a long time, cells, tissues, or the organism in general, are weakened and finally become fertile grounds for the proliferation of pathogens.
The application of the north pole (-) of the magnet on a tissue allows the cells to recover the lost electrons by reversing the oxidative processes, by balancing the positive and negative charges, this is the equivalent of leveling their pH, therefore, recovering their capacity of self-regulation and cell regeneration. Magnetic therapy must be accompanied, as we have already mentioned, by healthy lifestyle habits such as exercise, restful sleep and a proper diet; essential factors to maintain a balance of these factors (ions and radicals) in short: energy balance.
Complementary activities: